How to fix GPO – 16 Most Common Issues
Check out this post on how to fix GPO not applied to users and computers including the most 15 common causes and resolution.
Table of Content
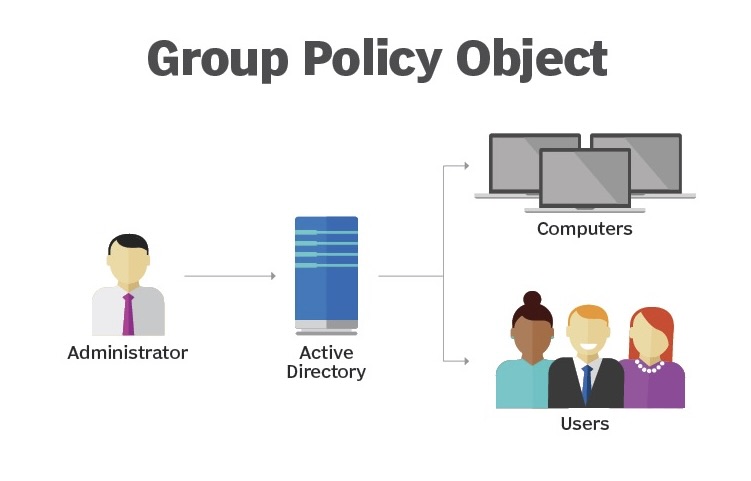
How to fix the 16 most common GPO issues for users and computers
- Check GPO Link and Scope:
- Ensure the GPO is linked to the correct Organizational Unit (OU) or domain where the users are located.
- Verify the GPO is enabled and not disabled at the link level.
- Ensure User Permissions:
- Check the Security Filtering settings in the GPO to ensure the users or groups have the “Read” and “Apply Group Policy” permissions.
- Check WMI Filters:
- If the GPO uses a WMI filter, verify that the filter criteria are correctly defined and apply to the users’ machines.
- Run GPUpdate:
- On the affected user’s machine, run
gpupdate /forcein Command Prompt to force a Group Policy refresh.
- On the affected user’s machine, run
- Check Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP):
- Use the
rsop.msctool or thegpresult /h report.htmlcommand to generate a Group Policy report. This will help identify which policies are applied and any errors.
- Use the
- Check Event Logs:
- Review the Event Viewer logs on the affected machine under “Application and Services Logs” > “Microsoft” > “Windows” > “GroupPolicy” for any Group Policy-related errors.
- Verify Network Connectivity:
- Ensure the affected user’s machine has proper network connectivity to the domain controllers.
- Replication Issues:
- Verify that all domain controllers are replicating correctly. Use the
repadmin /replsummarycommand to check for replication issues.
- Verify that all domain controllers are replicating correctly. Use the
- GPO Precedence:
- Ensure that no other conflicting GPOs with higher precedence are overriding the settings of the intended GPO.
- Check GPO Version:
- Make sure the GPO version is correct. If there are discrepancies, you might need to perform a Group Policy update or synchronization.
- Check for Loopback Processing:
- Ensure that loopback processing is configured correctly if it is in use. This setting can affect how user policies are applied.
- Ensure the GPO is not Corrupted:
- If you suspect the GPO might be corrupted, try creating a new GPO with the same settings and link it to the appropriate OU or domain.
- Review Local Group Policy:
- Local Group Policies can sometimes override domain policies. Check the local policies on the affected machines.
- Check for Slow Link Detection:
- Group Policy processing can be affected by slow network links. Ensure the network speed is sufficient for GPO processing.
- Update Group Policy Templates:
- Ensure that the administrative templates used in the GPO are up to date.
GPO still not applied to users?
However, if you have double checked the above causes, and still don’t know how to fix GPO issue not correctly applied to users, check out the following possible root cause and resolution.
Microsoft released in June 2016 a security update that has changed the way how a GPO is processed on client computers.
This security update aims to avoid an attacker to exploit a vulnerability between the communication of a domain controller and a computer.
Before MS16-072 was installed on your server, the user group policies were retrieved by using the user’s security context of the GPO. After MS16-072 is installed, user group policies are retrieved by using the computer’s security context of the GPO.
If you have removed the default “Authenticated Users” group from the security filtering of your GPO and set your custom security group containing the respective target users, you have removed as well the permission of “Read” from computers since they are members of this group too and consequently the policy will not work anymore.
How to fix it?
Simply adding either the “Authenticated Users” or “Domain Computers” group with the “Read” permissions on the Group Policy Objects “Delegation” tab. The purpose here is just to add “Read” permissions and not “Apply Group Policy” to the chosen group. You can keep using your custom security group in the security filtering tab as usual.
If you have too many GPO’s and applying the above workaround one by one is not an option, consider using the below script:
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/Powershell-script-to-cc281476
You can find further information here.
By following these steps, you should be able to diagnose and resolve issues preventing a GPO from being applied to users.
Still need help to fix GPO issues?
Running out of ideas and time on how to fix GPO in your environment?
Please, get in touch with me, I will be happy to provide a quick resolution for you on how to fix GPO with a fair price.
Check out more similar articles below
How to Migrate Files to SharePoint Online: 2025 Ultimate Guide
How to Migrate Files to SharePoint Online: 2025 Ultimate Guide Migrating your file shares to…
How to Configure App Protection Policies in Microsoft Intune
How to Configure App Protection Policies in Microsoft Intune In today’s business landscape, safeguarding sensitive…
Azure Cloud Migration for Beginners: A Practical 2025 Guide
Azure Cloud Migration for Beginners: A Practical 2025 Guide Moving your business to the cloud…
Ultimate Guide to How to Screenshot on a Computer Mac
Ultimate Guide to How to Screenshot on a Computer Mac For nearly two decades, I’ve…
SharePoint Site Building: A Complete Walkthrough for Your First Collection
SharePoint Site Building: A Complete Walkthrough for Your First Collection It is not very easy…
How to Enable MFA on Microsoft 365 for Better Security
How to Enable MFA on Microsoft 365 for Better Security Cybersecurity threats are on the…
For any doubts or suggestions, please leave a comment below.







Solved my problem by creating an OU and moving the computers in the “Computers” folder to the OU.
The policy was forest wide, enforced, no WMI filters, all you can do to force it put didn’t apply.
Thanks for your extense checklist.